Table of content
- Types of BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
- Procedure
- Risks and complications
- Pre-operation preparation
- Post-operative care
- Expected Results and recovery timeline
- Appointments and consultation
- Frequently asked questions
- Meet the team
- Pricing and payment plans
- Medical literature and research
- Support and counseling
- Send a message
LOSS OF VOLUME
INDICATION – BRIEF
Undereye puffiness, characterized by swelling under the eyes, can be influenced by both clinical and non-clinical factors. Clinically, aging leads to loss of skin elasticity and weakened muscles, causing fat to protrude. Genetic predisposition, fluid retention from conditions like kidney disease, allergies, and sinus infections also contribute. Lack of sleep and medical conditions such as dermatitis can exacerbate puffiness.
Non-clinical factors include lifestyle choices like high salt intake, alcohol and tobacco use, and poor diet. Environmental pollutants and climate changes can cause skin irritation and inflammation. Stress and cosmetic product irritation further contribute to the condition. Addressing undereye puffiness involves a holistic approach, including lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and cosmetic procedures, guided by a dermatologist.
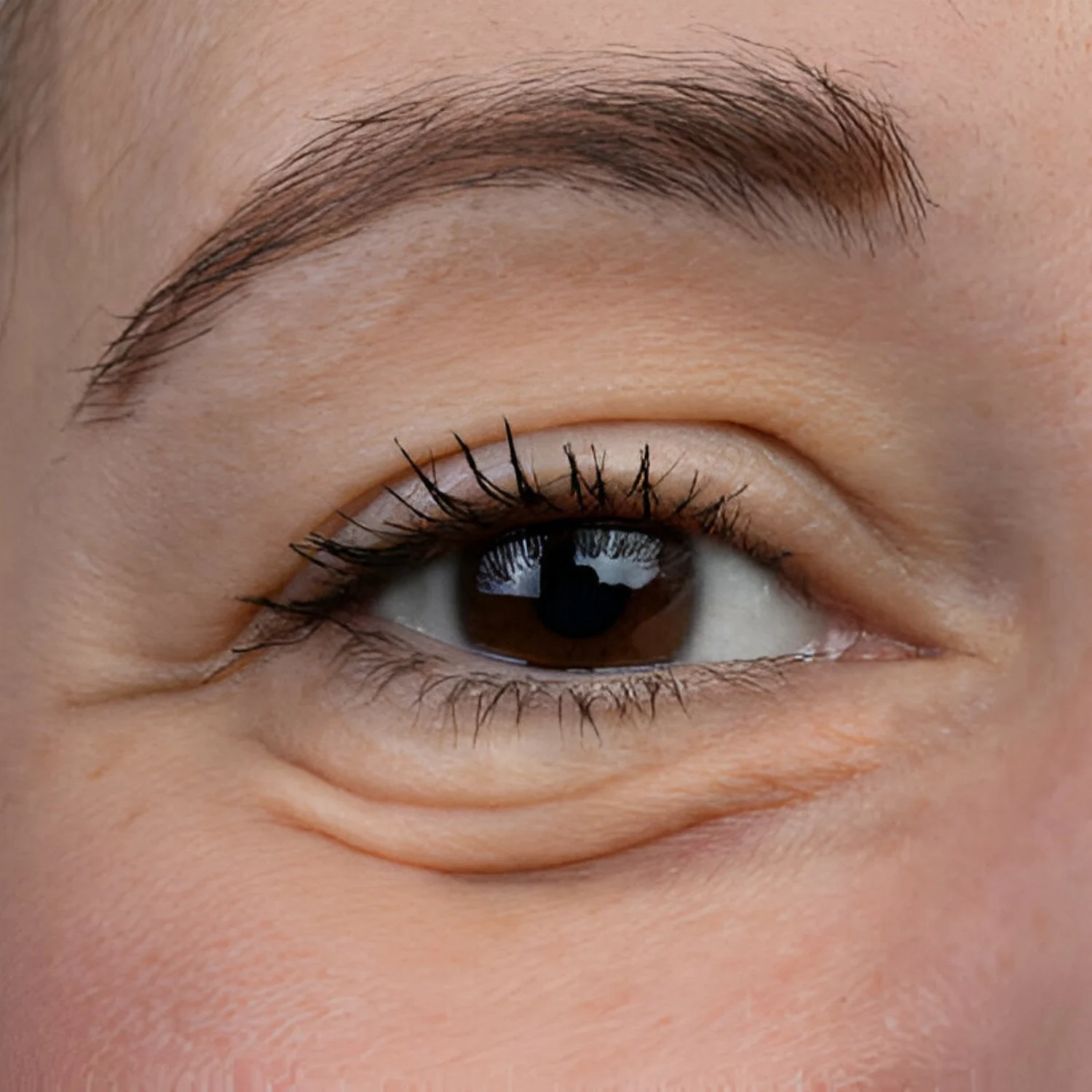
INDICATION – DEFINITION
Definition:
Undereye puffiness refers to swelling or puffiness in the area under the eyes, often accompanied by dark circles. This condition can be temporary or chronic and can affect both cosmetic appearance and, in some cases, the individual’s comfort and well-being.
Causal Factors:
Clinical Factors:
- Aging:
- Loss of skin elasticity: The skin under the eyes becomes thinner and less elastic with age, causing fat to protrude.
- Weakening of supporting muscles: Muscles around the eyes weaken, allowing fat to move into the lower eyelids.
- Genetics:
- Inherited traits: Family history of undereye puffiness can be a significant contributing factor.
- Fluid Retention:
- Edema: Conditions such as kidney disease or thyroid problems can cause fluid retention.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can lead to inflammation and fluid buildup under the eyes.
- Lack of Sleep:
- Sleep deprivation: Poor sleep patterns can cause blood vessels under the eyes to dilate, leading to puffiness.
- Medical Conditions:
- Sinus infections: Inflammation and congestion from sinus issues can lead to swelling around the eyes.
- Dermatitis: Skin conditions such as eczema can cause swelling and irritation.
Non-Clinical Factors:
- Lifestyle:
- Diet: High salt intake can cause fluid retention, exacerbating undereye puffiness.
- Alcohol and tobacco use: Both can lead to dehydration and poor circulation, worsening puffiness.
- Environmental Factors:
- Pollution: Exposure to environmental pollutants can cause skin irritation and inflammation.
- Climate: Changes in weather, particularly humidity and temperature, can impact skin hydration and cause puffiness.
- Cosmetic Products:
- Irritation from cosmetics: Certain skincare products and makeup can cause allergic reactions or irritation, leading to puffiness.
- Stress:
- Emotional stress: High stress levels can affect sleep quality and overall skin health, contributing to undereye puffiness.
Conclusion:
Undereye puffiness is a multifactorial condition influenced by a combination of clinical and non-clinical factors. Addressing this issue often requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and, in some cases, cosmetic procedures. Regular consultation with a dermatologist can help in identifying the underlying causes and formulating an effective treatment plan.
SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS
Symptoms:
- Swelling:
- Noticeable puffiness or swelling under the eyes, often more pronounced in the morning and may fluctuate throughout the day.
- Dark Circles:
- Accompanying dark circles or discoloration under the eyes, which can be due to the shadow cast by puffy eyelids or thinning skin revealing blood vessels.
- Loose or Sagging Skin:
- Skin under the eyes may appear loose, saggy, or baggy due to loss of skin elasticity.
- Mild Redness or Irritation:
- Some individuals may experience mild redness, itching, or irritation in the affected area.
- Tenderness:
- The area under the eyes may feel tender or sensitive to touch, especially if the puffiness is due to an underlying inflammatory condition.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination:
- A thorough examination of the undereye area, assessing the degree of swelling, skin texture, and presence of any accompanying symptoms such as redness or irritation.
- Patient History:
- Detailed patient history to identify potential contributing factors, including family history, lifestyle habits, sleep patterns, dietary intake, and any recent changes in cosmetic products.
- Allergy Testing:
- If allergies are suspected, specific allergy tests may be conducted to identify triggers that could be causing or exacerbating the puffiness.
- Blood Tests:
- Blood tests may be ordered to check for underlying conditions such as thyroid disorders, kidney function, or other systemic issues contributing to fluid retention.
- Imaging Studies:
- In certain cases, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs may be recommended to rule out sinus problems or other structural issues.
- Dermatoscopy:
- Dermatoscopy may be used to closely examine the skin for any signs of dermatological conditions like dermatitis or eczema that might be contributing to the puffiness.
- Consultation with Specialists:
- Referral to other specialists, such as an allergist or endocrinologist, may be necessary if an underlying medical condition is suspected.
Conclusion:
Diagnosing undereye puffiness involves a comprehensive approach that includes clinical examination, patient history, and targeted diagnostic tests. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective management and treatment. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Prognosis and Impact

Prognosis
- Varies by Cause:
- The prognosis for undereye puffiness largely depends on the underlying cause. For instance, puffiness due to lifestyle factors or temporary conditions like lack of sleep or fluid retention can often be resolved with appropriate lifestyle changes and treatments.
- Chronic Conditions:
- If puffiness is caused by chronic conditions such as allergies, thyroid issues, or genetic factors, it may persist and require ongoing management.
- Age-Related Changes:
- Age-related puffiness may not fully resolve without cosmetic interventions like fillers, laser treatments, or surgery (blepharoplasty).
- Management and Treatment:
- With proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plans, many patients experience significant improvement. Treatments might include topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and, if necessary, medical or surgical interventions.
Impact
- Cosmetic Concerns:
- Undereye puffiness can significantly affect a person’s appearance, leading to self-consciousness and reduced confidence. It can give an impression of fatigue or aging, even if the person feels well-rested and healthy.
- Psychological Effects:
- Persistent undereye puffiness can have psychological impacts, contributing to stress, anxiety, or depression, particularly if the individual feels dissatisfied with their appearance.
- Quality of Life:
- The cosmetic and psychological effects can indirectly impact overall quality of life, affecting social interactions, professional settings, and personal relationships.
- Comfort and Health:
- In some cases, undereye puffiness can cause physical discomfort, such as tenderness or irritation. If linked to allergies or sinus issues, it can also indicate underlying health problems that need attention.
- Treatment Burden:
- Managing chronic undereye puffiness may require ongoing treatments and lifestyle adjustments, which can be time-consuming and costly. This can add to the overall burden on the individual.
Conclusion
The prognosis for undereye puffiness is generally positive when the underlying cause is identified and appropriately managed. While the impact on appearance and self-esteem can be significant, effective treatments are available to mitigate these effects. A personalized approach, guided by a dermatologist, can help improve both the aesthetic and psychological outcomes for individuals experiencing undereye puffiness. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the treatment plan are essential for maintaining optimal results.
Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Modifications:
Sleep:
- Adequate Rest: Ensure sufficient sleep, typically 7-9 hours per night, to help reduce puffiness.
- Sleeping Position: Elevate the head during sleep to prevent fluid accumulation under the eyes.
Diet:
- Reduce Salt Intake: Lowering sodium in the diet can help minimize fluid retention.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and flush out excess salt from the body.
Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco:
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can prevent dehydration and subsequent puffiness.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can exacerbate puffiness and aging of the skin.
- Home Remedies:
Cold Compresses:
- Chilled Spoons or Cucumber Slices: Applying cold compresses to the undereye area can constrict blood vessels and reduce swelling.
Tea Bags:
- Caffeinated Tea Bags: Placing chilled, used tea bags over the eyes can help reduce puffiness due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Topical Treatments:
Eye Creams and Serums:
- Ingredients to Look For: Products containing caffeine, hyaluronic acid, retinol, peptides, and antioxidants can help reduce puffiness and improve skin elasticity.
Anti-Allergy Medications:
- Antihistamines: If puffiness is due to allergies, over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can be effective.
- Medical Treatments:
Prescription Creams:
- Hydrocortisone Cream: For inflammation-related puffiness, a dermatologist may prescribe a mild steroid cream.
Chemical Peels:
- Mild Peels: Chemical peels can improve skin texture and reduce dark circles that may accompany puffiness.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Dermal Fillers:
- Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Injectables like Restylane or Juvederm can help fill in hollow areas and reduce the appearance of puffiness.
Laser Therapy:
- Laser Resurfacing: Treatments like fractional laser can improve skin tone and texture, reducing puffiness and dark circles.
Microneedling:
- Collagen Induction Therapy: Microneedling can stimulate collagen production, improving skin firmness and reducing puffiness.
- Surgical Options:
Blepharoplasty:
- Eyelid Surgery: For severe, persistent undereye puffiness due to fat deposits, a surgical procedure to remove or reposition fat and tighten skin may be recommended.
- Additional Tips:
Sun Protection:
- Sunscreen: Regular use of sunscreen can prevent skin damage and premature aging around the eyes.
Gentle Skincare:
- Avoid Irritants: Use hypoallergenic skincare products to prevent irritation and inflammation.
Conclusion:
Treatment for undereye puffiness varies depending on the underlying cause and severity. A combination of lifestyle changes, home remedies, topical treatments, and medical or surgical interventions can effectively manage and reduce puffiness. Consulting with a dermatologist can help tailor a treatment plan specific to the individual’s needs, ensuring optimal results and long-term improvement. Regular follow-up and adjustments to the treatment plan are key to maintaining desired outcomes.
Risks and Side Effects
- Lifestyle Modifications
Sleep:
- Risk: Minimal risk, but inadequate sleep can negate benefits.
- Side Effects: Improved sleep may reduce stress and overall health.
Diet:
- Risk: Minimal risk, but requires consistent dietary changes.
- Side Effects: Improved hydration and reduced salt intake can benefit overall health.
Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco:
- Risk: Withdrawal symptoms for heavy users.
- Side Effects: Improved skin health and reduced risk of other health issues.
- Home Remedies
Cold Compresses:
- Risk: Potential skin irritation from prolonged cold exposure.
- Side Effects: Temporary relief of puffiness.
Tea Bags:
- Risk: Allergic reactions to tea components.
- Side Effects: Reduced puffiness and inflammation.
- Topical Treatments
Eye Creams and Serums:
- Risk: Allergic reactions or skin irritation.
- Side Effects: Possible stinging, redness, or dryness.
Anti-Allergy Medications:
- Risk: Drowsiness, dry mouth, or other systemic effects.
- Side Effects: Reduced allergic symptoms and puffiness.
- Medical Treatments
Prescription Creams:
- Risk: Skin thinning or irritation with prolonged use.
- Side Effects: Temporary redness or dryness.
Chemical Peels:
- Risk: Skin irritation, peeling, or hyperpigmentation.
- Side Effects: Improved skin texture and reduced dark circles.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
Dermal Fillers:
- Risk: Bruising, swelling, or allergic reactions.
- Side Effects: Temporary redness, tenderness, or lumps at injection site.
Laser Therapy:
- Risk: Burns, scarring, or changes in skin pigmentation.
- Side Effects: Temporary redness, swelling, or sensitivity.
Microneedling:
- Risk: Infection, skin irritation, or pigmentation changes.
- Side Effects: Temporary redness, swelling, or discomfort.
- Surgical Options
Blepharoplasty:
- Risk: Infection, scarring, or complications from anesthesia.
- Side Effects: Swelling, bruising, or changes in eyelid contour.
- Additional Tips
Sun Protection:
- Risk: Minimal risk, though improper application can reduce effectiveness.
- Side Effects: Potential for allergic reaction to sunscreen ingredients.
Gentle Skincare:
- Risk: Allergic reactions to new products.
- Side Effects: Improved skin health with appropriate products.
Conclusion:
Each treatment option for undereye puffiness carries its own risks and potential side effects. It is crucial to consider these factors when selecting a treatment plan. Consulting with a dermatologist can help tailor the approach to minimize risks and maximize benefits, ensuring safe and effective management of undereye puffiness. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor the treatment’s progress and adjust as necessary.
FAQ Section
Undereye puffiness can be caused by a variety of factors including aging, genetics, fluid retention, allergies, lack of sleep, high salt intake, and lifestyle choices like alcohol and tobacco use. It can also be influenced by medical conditions such as thyroid problems and sinus infections.
While it may not always be preventable, you can reduce the risk by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Ensure adequate sleep, stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet low in salt, avoid alcohol and tobacco, manage allergies, and use gentle skincare products. Protecting your skin from the sun and reducing stress can also help.
Effective home remedies include applying cold compresses, using chilled tea bags, getting adequate sleep, staying hydrated, and reducing salt intake. Elevating your head during sleep and using hypoallergenic skincare products can also be beneficial.
Yes, there are various over-the-counter eye creams and serums that contain ingredients like caffeine, hyaluronic acid, retinol, peptides, and antioxidants which can help reduce puffiness. Antihistamines can also be effective if allergies are contributing to the puffiness.
If home remedies and over-the-counter treatments do not reduce the puffiness, or if it is accompanied by pain, severe redness, or other unusual symptoms, it is advisable to see a dermatologist. Persistent undereye puffiness could indicate an underlying medical condition that requires professional evaluation.
Medical treatments include prescription creams, chemical peels, dermal fillers, laser therapy, and microneedling. In more severe cases, surgical options like blepharoplasty may be recommended. A dermatologist can help determine the best treatment based on the underlying cause and severity of the puffiness.
Most treatments carry some risks or side effects. Topical treatments can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. Minimally invasive procedures like fillers and laser therapy can lead to bruising, swelling, or changes in skin pigmentation. Surgical procedures carry risks such as infection and scarring. It’s important to discuss potential risks with your dermatologist before starting any treatment.
The time to see results varies depending on the treatment. Home remedies and over-the-counter products may take several weeks to show noticeable improvements. Medical treatments like fillers or laser therapy can provide quicker results, often within a few days to weeks. Surgical procedures typically have a longer recovery time, but results are more permanent.
In some cases, undereye puffiness can be a sign of an underlying health condition, such as thyroid problems, kidney disease, or severe allergies. If puffiness is persistent, worsening, or accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice for a thorough evaluation.
Yes, several lifestyle changes can help reduce undereye puffiness. These include getting sufficient sleep, reducing salt intake, staying hydrated, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, managing stress, and protecting your skin from the sun. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can also contribute to overall skin health and reduce puffiness.
