Table of content
- Types of BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
- Procedure
- Risks and complications
- Pre-operation preparation
- Post-operative care
- Expected Results and recovery timeline
- Appointments and consultation
- Frequently asked questions
- Meet the team
- Pricing and payment plans
- Medical literature and research
- Support and counseling
- Send a message
LOSS OF VOLUME
INDICATION – BRIEF
Undereye dark circles are a common cosmetic concern characterized by darkened skin under the eyes, influenced by both clinical and non-clinical factors. Clinically, genetic predisposition, periorbital hyperpigmentation, structural and vascular factors, and aging play significant roles. Genetically, family history and ethnic background can predispose individuals, while conditions like dermatitis can cause increased melanin production. Structural issues like thin skin and loss of subcutaneous fat, along with aging-related collagen loss, contribute to the appearance of dark circles. Non-clinical factors include lifestyle choices such as lack of sleep, stress, smoking, and alcohol consumption, which can exacerbate dark circles. Nutritional deficiencies, allergies, sun exposure, and dehydration also contribute. Effective management involves addressing these diverse causes through lifestyle changes, topical treatments, and medical procedures.
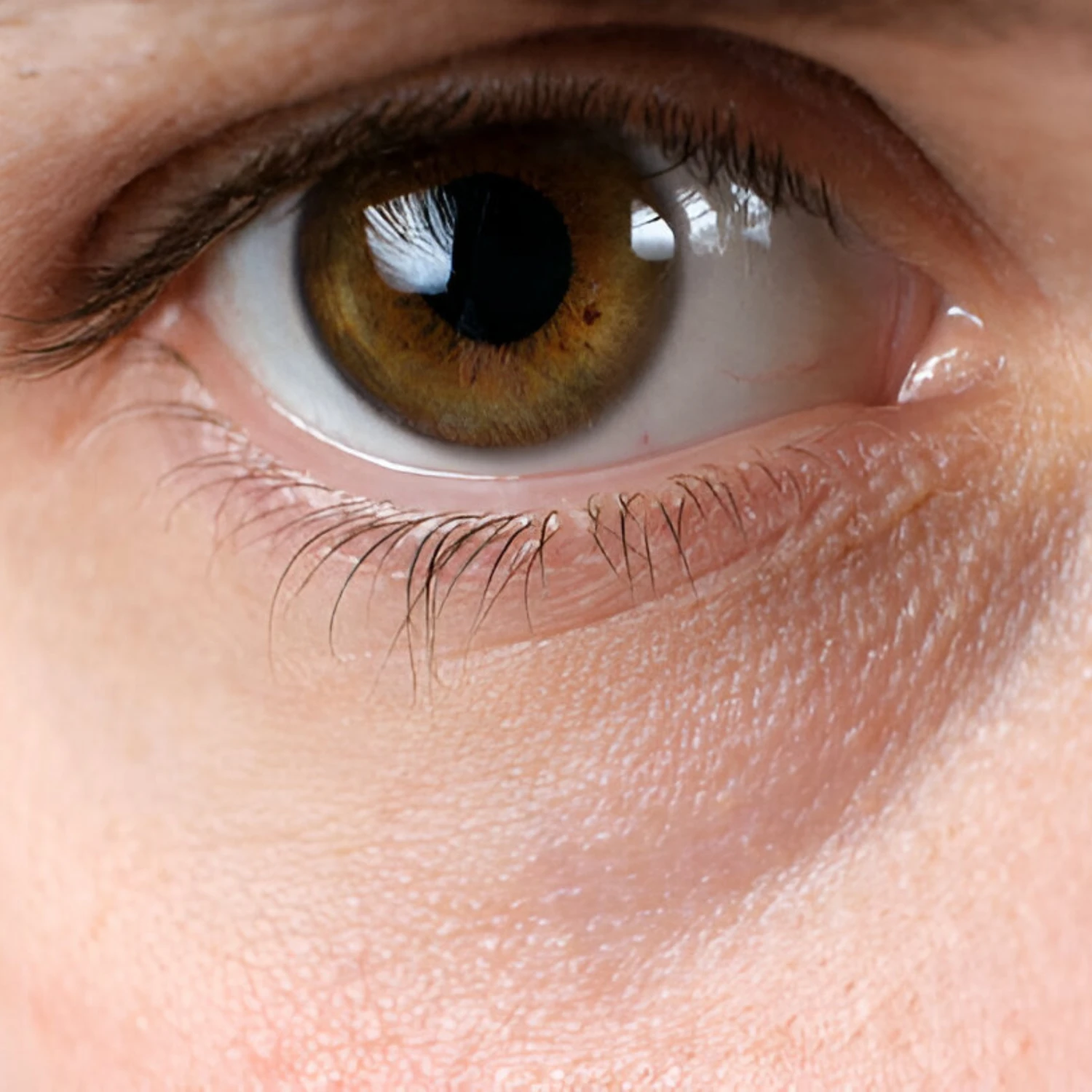
INDICATION – DEFINITION
Indication: Undereye dark circles are a common cosmetic concern characterized by darkened skin under the eyes. They can affect individuals of all ages and skin types, often leading to a tired and aged appearance.
Causal Factors:
Clinical Factors
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Family history of dark circles can indicate a genetic tendency.
- Ethnic background, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones, can influence the prominence of dark circles.
- Periorbital Hyperpigmentation:
- Increased melanin production in the periorbital area.
- Can result from conditions such as atopic or allergic contact dermatitis.
- Structural and Vascular Factors:
- Thin skin under the eyes, which can reveal underlying blood vessels.
- Blood pooling in the under-eye area due to poor circulation or venous congestion.
- Tear trough deformity or loss of subcutaneous fat, leading to shadowing and dark appearance.
- Aging:
- Loss of collagen and fat with age, leading to hollowing and shadowing.
- Thinning of the skin exacerbates the appearance of underlying vessels and pigmentation.
Non-Clinical Factors
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors:
- Lack of sleep or poor sleeping habits, causing fluid retention and darkening.
- Chronic stress, leading to increased cortisol levels and skin changes.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, which can dehydrate the skin and exacerbate pigmentation.
- Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Deficiencies in vitamins such as Vitamin C, K, and iron can contribute to the appearance of dark circles.
- Allergic Reactions:
- Allergies leading to rubbing of the eyes, causing skin irritation and hyperpigmentation (allergic shiners).
- Sun Exposure:
- UV radiation can lead to increased melanin production and exacerbate hyperpigmentation in the periorbital area.
- Dehydration:
- Lack of sufficient hydration can cause the skin under the eyes to appear dull and sunken.
Conclusion
Undereye dark circles are multifactorial, with both clinical and non-clinical elements contributing to their development. Understanding these factors is essential for effective management and treatment, which may include lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, medical procedures, or a combination of these approaches.
SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS
Symptoms:
- Darkened Skin Under the Eyes:
- The primary symptom is the presence of darker pigmentation under the eyes compared to the surrounding facial skin. This discoloration can range from light brown to dark brown, blue, purple, or even black, depending on the underlying cause and individual skin type.
- Hollow or Sunken Appearance:
- Some individuals may notice a hollow or sunken look under the eyes, often due to the loss of subcutaneous fat and collagen as part of the aging process.
- Shadowing:
- Shadowing under the eyes can occur due to structural variations such as tear trough deformity, which can create the illusion of darker circles.
- Puffy or Swollen Appearance:
- In some cases, fluid retention can cause puffiness or swelling under the eyes, contributing to the appearance of dark circles.
- Accompanying Skin Conditions:
- Other symptoms might include dryness, itching, or redness, especially if the dark circles are associated with dermatitis or allergies.
Diagnosis:
- Patient History:
- A thorough patient history is essential, including inquiries about family history, lifestyle factors (such as sleep patterns, stress levels, smoking, and alcohol consumption), and any history of allergies or skin conditions.
- Physical Examination:
- A detailed physical examination of the periorbital area is conducted to assess the color, depth, and extent of the dark circles. The examination may also include checking for signs of fluid retention, puffiness, or structural abnormalities.
- Dermatoscopy:
- Dermatoscopy can be used to examine the skin more closely, helping to identify pigmentation patterns and vascular involvement.
- Allergy Testing:
- If allergies are suspected, appropriate allergy tests may be performed to identify potential allergens contributing to dark circles.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests might be ordered to check for nutritional deficiencies (e.g., iron, vitamin B12, vitamin K) or underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the dark circles.
- Imaging Studies:
- In rare cases, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI might be considered to evaluate deeper structural issues or vascular anomalies.
Conclusion
Diagnosing undereye dark circles involves a comprehensive approach that includes evaluating symptoms, taking a detailed patient history, and conducting various examinations and tests. This holistic assessment helps in identifying the underlying causes and developing an effective treatment plan.
Prognosis and Impact

Prognosis
- Chronic Nature:
- Undereye dark circles are often chronic and may persist without appropriate intervention. The prognosis largely depends on the underlying cause and the individual’s response to treatment.
- Variable Outcomes:
- With targeted treatment and lifestyle modifications, many individuals can experience significant improvement. However, complete resolution may not always be possible, especially if genetic or structural factors are predominant.
- Treatment Response:
- Non-invasive treatments like topical creams, lifestyle changes, and sun protection can yield positive results for mild cases. For more severe cases, medical treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and fillers may be more effective. The response to treatment varies from person to person.
- Maintenance:
- Long-term maintenance is often necessary to prevent recurrence. This includes continuous use of skincare products, sun protection, and healthy lifestyle practices.
Impact
- Aesthetic Concerns:
- Dark circles can significantly affect an individual’s appearance, leading to a tired, aged, or unhealthy look. This is often the primary concern for most patients seeking treatment.
- Psychosocial Impact:
- The presence of dark circles can lead to reduced self-esteem and confidence. Individuals may feel self-conscious about their appearance, which can impact social interactions and professional life.
- Quality of Life:
- Persistent dark circles can affect overall quality of life. The psychological burden can lead to increased stress and anxiety, which might further exacerbate the condition.
- Economic Impact:
- The cost of treatments, both non-invasive and medical, can be significant. Long-term maintenance and multiple treatment sessions can add up, making it a financial consideration for many patients.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Patients may need to adopt lifestyle changes, such as improved sleep hygiene, dietary adjustments, and stress management techniques, which can have a positive overall impact on their health.
Conclusion
The prognosis for undereye dark circles varies based on the underlying cause and treatment approach. While many individuals can see significant improvement, complete resolution may require ongoing management. The impact of dark circles extends beyond aesthetics, affecting psychological well-being, quality of life, and economic factors. A comprehensive and personalized treatment plan is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.
Treatment Options
Treatment Options for Undereye Dark Circles
Topical Treatments
- Brightening Creams:
- Ingredients like Vitamin C, niacinamide, and licorice extract help reduce pigmentation and brighten the skin.
- Retinoids:
- Topical retinoids stimulate collagen production, improve skin texture, and reduce the appearance of dark circles.
- Hydroquinone:
- A skin-lightening agent that reduces hyperpigmentation but should be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects.
- Caffeine-based Creams:
- Caffeine constricts blood vessels, reducing puffiness and dark appearance under the eyes.
- Peptides:
- Peptides enhance collagen production and skin elasticity, helping to reduce dark circles and fine lines.
Medical Treatments
- Chemical Peels:
- Mild chemical peels with glycolic acid or lactic acid can exfoliate the skin, improve texture, and lighten pigmentation.
- Laser Therapy:
- Fractional lasers or intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments target pigmentation and stimulate collagen production, improving skin appearance.
- Dermal Fillers:
- Hyaluronic acid fillers can be injected into the tear trough area to address volume loss and reduce shadowing.
- Microneedling:
- Microneedling with radiofrequency or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture.
- Carboxytherapy:
- This involves injecting carbon dioxide gas into the skin to improve circulation and reduce dark circles.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Adequate Sleep:
- Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can help reduce the appearance of dark circles.
- Hydration:
- Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin hydration and elasticity.
- Cold Compresses:
- Applying cold compresses or chilled cucumber slices can reduce puffiness and dark circles.
- Healthy Diet:
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins (especially Vitamin C, K, and iron) supports skin health and reduces dark circles.
- Sun Protection:
- Using sunscreen and wearing sunglasses can prevent UV-induced pigmentation around the eyes.
Preventive Measures
- Avoid Rubbing Eyes:
- Rubbing can irritate the skin and worsen pigmentation.
- Manage Allergies:
- Treating allergies can reduce the tendency to rub the eyes and prevent dark circles from worsening.
- Stress Management:
- Techniques like meditation, yoga, and regular exercise can reduce stress, which may contribute to dark circles.
Combination Therapy
- Often, a combination of treatments provides the best results. For example, using topical treatments in conjunction with medical procedures can enhance overall effectiveness.
Conclusion
Treatment options for undereye dark circles range from topical treatments and medical procedures to lifestyle changes and preventive measures. A comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s specific condition and underlying causes typically yields the best results. Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial to develop a personalized treatment plan that effectively addresses the patient’s needs and concerns.
Risks and Side Effects
Topical Treatments
- Brightening Creams:
- Risks: Minimal
- Side Effects: Possible irritation or allergic reactions, especially in sensitive skin types. Patch testing is recommended before use.
- Retinoids:
- Risks: Moderate
- Side Effects: Redness, peeling, dryness, and increased sensitivity to sunlight. Gradual introduction and use of sunscreen are advised.
- Hydroquinone:
- Risks: Moderate to high
- Side Effects: Skin irritation, redness, and potential for ochronosis (a bluish-black discoloration with long-term use). Should be used under medical supervision.
- Caffeine-based Creams:
- Risks: Low
- Side Effects: Rare allergic reactions or skin irritation.
- Peptides:
- Risks: Low
- Side Effects: Mild irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
Medical Treatments
- Chemical Peels:
- Risks: Moderate
- Side Effects: Redness, peeling, dryness, and potential for hyperpigmentation or scarring if not performed correctly. Sunscreen use is necessary post-treatment.
- Laser Therapy:
- Risks: Moderate to high
- Side Effects: Redness, swelling, blistering, changes in skin pigmentation (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation), and rare scarring. Multiple sessions may be required, and strict sun protection is necessary.
- Dermal Fillers:
- Risks: Moderate
- Side Effects: Bruising, swelling, redness, lumps, asymmetry, and rare complications like vascular occlusion (blocked blood vessels). Should be performed by an experienced practitioner.
- Microneedling:
- Risks: Moderate
- Side Effects: Redness, swelling, bruising, and potential for infection if not done under sterile conditions. Rarely, it can cause scarring.
- Carboxytherapy:
- Risks: Low to moderate
- Side Effects: Bruising, swelling, discomfort at the injection site, and rare cases of infection. Temporary side effects usually resolve within a few days.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Adequate Sleep:
- Risks: None
- Side Effects: None
- Hydration:
- Risks: None
- Side Effects: None
- Cold Compresses:
- Risks: Low
- Side Effects: Temporary redness or irritation if applied for too long.
- Healthy Diet:
- Risks: None
- Side Effects: None
- Sun Protection:
- Risks: Low
- Side Effects: Potential allergic reactions to sunscreen ingredients. Patch testing recommended for sensitive skin.
Preventive Measures
- Avoid Rubbing Eyes:
- Risks: None
- Side Effects: None
- Manage Allergies:
- Risks: Low
- Side Effects: Potential side effects from allergy medications, such as drowsiness or dry mouth. Consult with a healthcare provider.
- Stress Management:
- Risks: None
- Side Effects: None
Combination Therapy
- Risks: Variable depending on the treatments combined.
- Side Effects: Combining treatments can amplify individual side effects or lead to unexpected reactions. Close monitoring by a dermatologist is essential.
Conclusion
Each treatment option for undereye dark circles comes with its own set of risks and potential side effects. It’s crucial to evaluate these factors carefully and consult with a dermatologist to choose the most appropriate and safe treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs and skin type. Regular follow-ups and adherence to post-treatment care are essential to minimize risks and enhance treatment outcomes.
FAQ Section
Undereye dark circles can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, aging, lack of sleep, allergies, dehydration, excessive sun exposure, and certain medical conditions. Lifestyle factors like smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress can also contribute.
While undereye dark circles are usually a cosmetic concern, they can sometimes indicate underlying health issues such as allergies, nutritional deficiencies, or chronic fatigue. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you’re concerned.
Prevention tips include getting adequate sleep, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, managing allergies, protecting your skin from the sun with sunscreen, and avoiding rubbing your eyes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and stress management can also help.
Treatment options vary depending on the cause and severity. They include topical treatments (e.g., brightening creams, retinoids), medical procedures (e.g., chemical peels, laser therapy, dermal fillers), and lifestyle changes (e.g., improved sleep, hydration). Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the best approach for you.
Some home remedies, such as applying cold compresses, using cucumber slices, and getting enough sleep, can help reduce the appearance of dark circles. However, their effectiveness varies, and they may not work for everyone. For persistent dark circles, professional treatments may be more effective.
Yes, a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can improve skin health and potentially reduce dark circles. Specifically, vitamins C, K, and iron are beneficial. Staying hydrated is also important for maintaining skin elasticity and reducing puffiness.
Genetics can play a significant role in the development of undereye dark circles. If your family members have dark circles, you may be more likely to have them as well. Genetic factors can influence skin pigmentation, blood vessel visibility, and fat distribution around the eyes.
The timeline for seeing results varies depending on the treatment. Topical treatments may take several weeks to months to show improvement, while medical procedures like laser therapy or fillers can offer more immediate results. Consistency and following a dermatologist’s recommendations are key.
Yes, each treatment has its own set of risks and potential side effects. Topical treatments may cause irritation or allergic reactions, while medical procedures can involve redness, swelling, and in rare cases, more serious complications. It’s important to discuss these risks with a dermatologist.
Makeup can be an effective temporary solution for covering undereye dark circles. Concealers and color correctors are specifically designed to mask discoloration. Choosing the right shade and formulation for your skin type is crucial for a natural look.
Look for a board-certified dermatologist with experience in treating undereye dark circles. Reading reviews, asking for recommendations, and scheduling a consultation to discuss your concerns and treatment options can help you find the right specialist.
Combining treatments can be effective but should be done under the guidance of a dermatologist to avoid adverse reactions and ensure compatibility. A professional can create a tailored treatment plan that maximizes benefits while minimizing risks.
