Table of content
- Types of BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
- Procedure
- Risks and complications
- Pre-operation preparation
- Post-operative care
- Expected Results and recovery timeline
- Appointments and consultation
- Frequently asked questions
- Meet the team
- Pricing and payment plans
- Medical literature and research
- Support and counseling
- Send a message
HAIR GROWTH
INDICATION – BRIEF
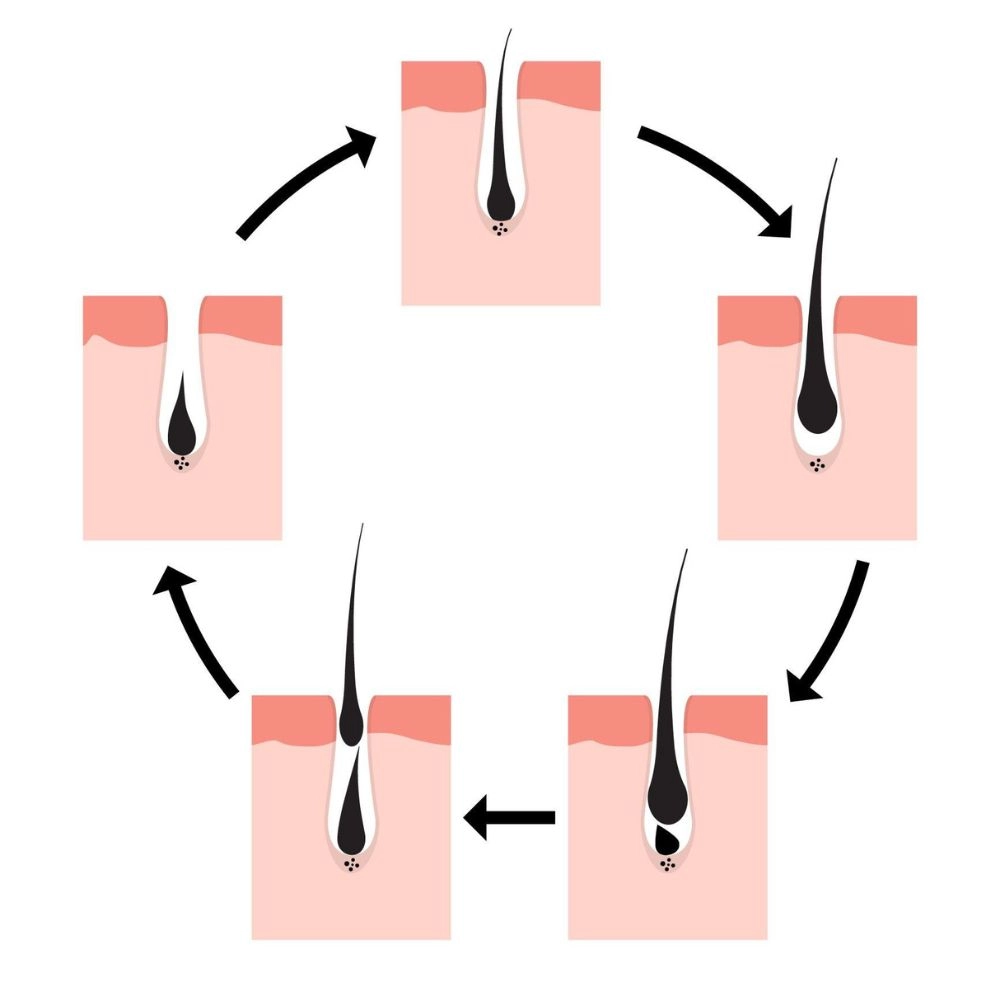
Hair growth, a process involving the anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting) phases, is affected by both clinical and non-clinical factors. Clinically, genetics, age, hormonal changes, health conditions, and certain medications can influence hair growth and loss. Non-clinical factors include diet, stress, hair care practices, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. For instance, a diet lacking in essential nutrients or high-stress levels can impair hair growth, while harmful hair care practices and smoking can lead to hair loss. Conversely, a healthy diet and regular exercise can promote hair health. To address hair growth issues, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist.
INDICATION – DEFINITION
Hair growth is a complex process that involves several phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). On average, hair typically grows about half an inch per month. However, this can vary widely based on a range of clinical and non-clinical factors.
Clinical factors
- Genetics: One’s genetic makeup significantly influences their hair growth rate, hair type (straight, wavy, curly), and when they might begin experiencing hair loss.
- Age: As people age, their rate of hair growth can slow down. This is due in part to cells gradually losing their regenerative ability, and hair follicles becoming less active.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones play a crucial role in hair growth. For example, hormones can impact the hair growth cycle during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also affect hair growth and may lead to conditions like hirsutism (excessive hair growth) or alopecia (hair loss).
- Health Conditions: Certain diseases and health conditions can impact hair growth. For instance, alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss. Thyroid disorders can also affect hair growth.
- Medications and Treatments: Some medicines, like chemotherapy drugs, can lead to hair loss by disrupting the hair growth cycle.
Non-clinical factors
- Diet and Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients like vitamins A, C, D, E, and B vitamins (especially biotin), as well as proteins and omega-3 fatty acids, can impair hair growth and lead to hair loss.
- Stress: Significant stress can push hair follicles into the telogen phase, leading to increased hair shedding, a condition known as telogen effluvium.
- Hair Care Practices: Certain hair care practices can also impact hair growth. Overstyling, using heat tools, or harsh products can damage hair and potentially affect its growth.
- Lifestyle: Smoking has been associated with baldness in men, while excessive alcohol can lead to nutrient deficiencies affecting hair health. Regular exercise, on the other hand, can help by improving overall circulation, including to the scalp.
- Environment: Environmental factors like exposure to UV rays can damage the hair. Seasonal changes also influence hair growth, with some studies suggesting hair grows faster in summer than in winter.
If there are issues with hair growth, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or a healthcare professional. They can identify the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include changes in diet or hair care practices, stress management techniques, or potentially medical treatments.
SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS
Symptoms
Abnormalities in hair growth typically present as either excessive hair growth (hirsutism) or hair loss (alopecia).
- Hirsutism: Excessive or unwanted hair that grows on a woman’s body and face is the primary symptom of hirsutism. The hair is usually thick and dark, rather than fine and light.
- Alopecia: Alopecia, or hair loss, can occur in many different patterns. It may be localized to one area, like in alopecia areata, or affect the entire scalp as in androgenetic alopecia (pattern hair loss). Symptoms can include gradual thinning on top of the head, bald spots, or full-body hair loss. Other symptoms may also be present, such as itching or burning.
Diagnosis
A dermatologist will use several methods to diagnose the cause of abnormal hair growth:
- Medical History: Gathering a comprehensive medical history is the first step. This includes discussing family history, dietary habits, medication use, lifestyle habits, and the duration and pattern of symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A detailed examination of the scalp and hair can often give clues about the type of hair loss. The pattern and extent of hair loss, the presence of broken hairs, redness, scaling, or inflammation all provide useful information.
- Blood Tests: If a hormonal imbalance is suspected as a cause, blood tests can be useful. They can check levels of various hormones, or possibly other indicators of health like thyroid function.
- Scalp Biopsy: In certain cases, a scalp biopsy may be necessary. This involves removing a small section of skin from the scalp to be examined under a microscope, allowing the doctor to check the hair follicles directly.
- Pull Test: The pull test involves gentle traction on a section of hair to see how many hairs come out. This helps determine the stage of the shedding process.
- Trichoscopy: A dermoscope can be used to visualize the scalp and hair fibers at high magnification, providing detailed insights about the hair follicles, shafts, and scalp.
Based on the symptoms and diagnosis, a dermatologist can determine the cause of the hair growth issue and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Prognosis and Impact

Prognosis
- Hirsutism: Hirsutism, or excessive hair growth, due to hormonal imbalances like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can often be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, or procedures like electrolysis or laser hair removal. While hirsutism can be a chronic condition, the prognosis is generally good with appropriate management.
- Alopecia: The prognosis for alopecia, or hair loss, varies significantly based on the type. Androgenetic alopecia, or pattern hair loss, is a progressive condition that typically worsens over time. Meanwhile, alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition, often has a more unpredictable course, with hair loss and regrowth occurring in cycles. Some types of hair loss may be reversible, while others may be permanent.
Impact
Hair growth disorders can have a significant psychological and emotional impact. Hair is often associated with beauty and personal identity, so hair disorders can lead to reduced self-esteem and confidence.
- Emotional Impact: Hair loss can cause significant distress, including feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, and depression. These feelings can impact social interactions and overall quality of life.
- Social Impact: Society often places a significant emphasis on appearance, and hair plays a major role in that. Changes in hair can lead to negative societal perceptions, which can impact relationships and career opportunities.
- Economic Impact: The financial cost of managing hair growth disorders can be substantial, considering the price of medications, treatments, wigs, or hairpieces.
Treatment Options
Hirsutism Treatment
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight may help to reduce the amount of hair growth.
- Hair Removal Techniques: Waxing, shaving, plucking, or using depilatory creams can help control excessive hair growth.
- Laser Hair Removal/Electrolysis: These procedures use heat to damage hair follicles and reduce hair growth.
- Medications: Certain medications can help reduce hair growth, such as birth control pills (which can adjust hormone levels) and anti-androgens like spironolactone.
Alopecia Treatment
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter medication can help stimulate hair growth in both men and women.
- Finasteride (Propecia): This prescription medication is used to treat pattern baldness in men.
- Corticosteroids: These are often used for hair loss due to autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata. They can be applied topically, injected into the scalp, or taken orally.
- Anthralin: This is a topical medication used to alter the skin’s immune function.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: This is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body to the balding area.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy (PRP): This is a newer treatment that involves injecting the scalp with plasma from your own blood to stimulate hair growth.
Keep in mind, the effectiveness of treatments varies between individuals. It may take some time to see significant changes, and some treatments may have side effects. It is recommended to discuss these factors with your dermatologist to understand the best options for you.
Risks and Side Effects
Hirsutism Treatment
- Lifestyle Changes: There are minimal risks associated with maintaining a healthy lifestyle, but rapid weight loss can sometimes exacerbate hair loss.
- Hair Removal Techniques: These can lead to skin irritation, ingrown hairs, and folliculitis. They are also temporary and require ongoing treatment.
- Laser Hair Removal/Electrolysis: Risks include skin irritation, changes in skin color, scarring, and potential eye injury if performed improperly on facial hair.
- Medications: Birth control pills can increase the risk of blood clots, high blood pressure, and may have other side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, and nausea. Anti-androgens like spironolactone can cause dry skin, heartburn, and fatigue, and are generally avoided in men due to the risk of feminizing effects.
Alopecia Treatment
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Side effects can include scalp irritation, unwanted hair growth on adjacent areas like the face and hands, and rapid heart rate.
- Finasteride (Propecia): Risks include decreased libido, potential erectile dysfunction, and in rare cases, male breast cancer. It should not be handled by women who are or may become pregnant, as it can cause birth defects.
- Corticosteroids: These can lead to skin thinning, changes in skin color, easy bruising, and stretch marks when applied topically. Injection can cause temporary depressions in the skin. Oral corticosteroids have many potential side effects, including osteoporosis, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cataracts.
- Anthralin: This can irritate skin and stain skin and clothing.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: As with any surgery, risks include infection, scarring, and anesthesia complications. The new hair follicles could also be rejected, or the aesthetic result may not be as expected.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy (PRP): Risks are generally minimal but can include injury from the injection, infection, scar tissue formation, and calcification at the injection points.
It’s essential to discuss potential risks and side effects with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision about the best course of treatment for you.
FAQ Section
Hair grows in cycles including growth (anagen), transitional (catagen), and resting (telogen) phases. Several factors like genetics, age, hormones, health conditions, diet, stress, hair care practices, lifestyle, and environment can influence hair growth.
Abnormal hair growth can present as excessive hair growth (hirsutism), particularly in women, or hair loss (alopecia). Symptoms may vary, ranging from thick, dark hair growth in unexpected areas to bald patches or diffuse hair thinning.
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and possibly blood tests to check hormone levels or other indicators. In some cases, a scalp biopsy or trichoscopy may be performed.
Treatment options vary depending on the cause. They may include lifestyle changes, hair removal techniques, laser/electrolysis, medications, hair transplant surgery, or newer treatments like platelet-rich plasma therapy.
Yes, treatments can have side effects, ranging from minor irritation to more significant risks. It’s important to discuss these with your healthcare provider to understand the potential benefits and risks.
Prognosis varies depending on the cause. While some conditions, like pattern hair loss, may progressively worsen, others can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment.
Hair growth disorders can have a significant psychological and emotional impact, affecting self-esteem and social interactions. They can also impose a financial burden due to the costs of treatments.
Absolutely. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, along with a healthy lifestyle including regular exercise, can contribute positively to hair growth and overall hair health.
